We have experienced the cases when customers considered high precision reduction gears TwinSpin® and their functioning principle the same as the principle of Strain Wave reduction gears /further in the text as „SW“/.
TwinSpin® principle-based reduction gears
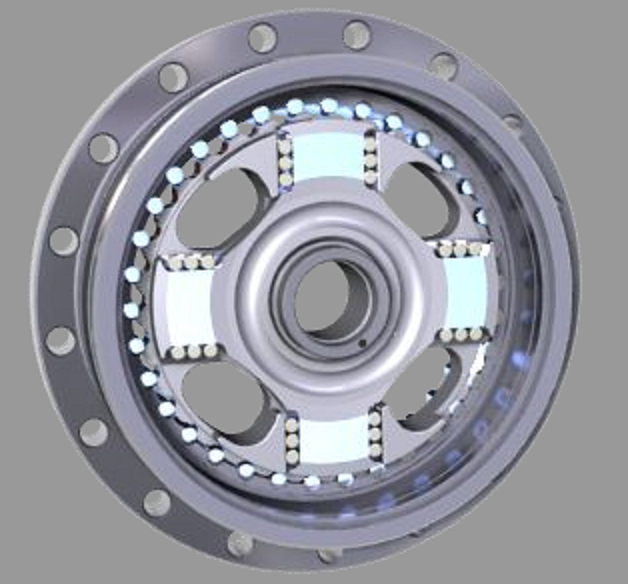
Figure No. 1 shows reduction principle TwinSpin® where the input shaft with excenters excites planetary movement of cycloidal wheels which are meshing with grooves in the case. The crosses are acting as the members transforming planetary movement of cycloidal gears to the rotary motion of pair of flanges. The transmission members are encapsulated in the case.
Figure No. 1
Strain Wave principle-based reduction gears
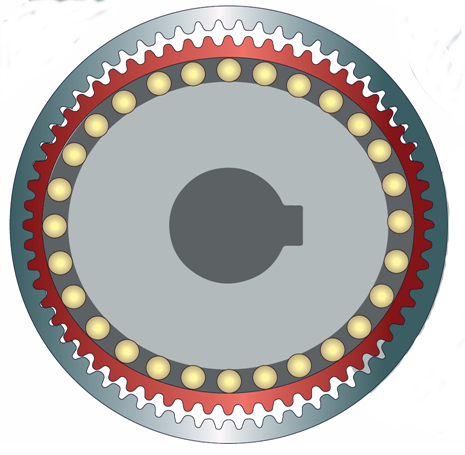
Figure No. 2 shows reduction principle SW where elliptical unit – wave generator with elliptical bearing is joined with a deformed unit called flex spline, which is copying the generator shape and rigid circular spline with internal toothing where flex spline meshes into. The reduction is accomplished through a tooth count differential between the flex spline and the circular spline. For every full rotation of the wave generator, the flex spline rotates less in the backward direction because it has fewer teeth than the rigid circular spline.
Figure No. 2
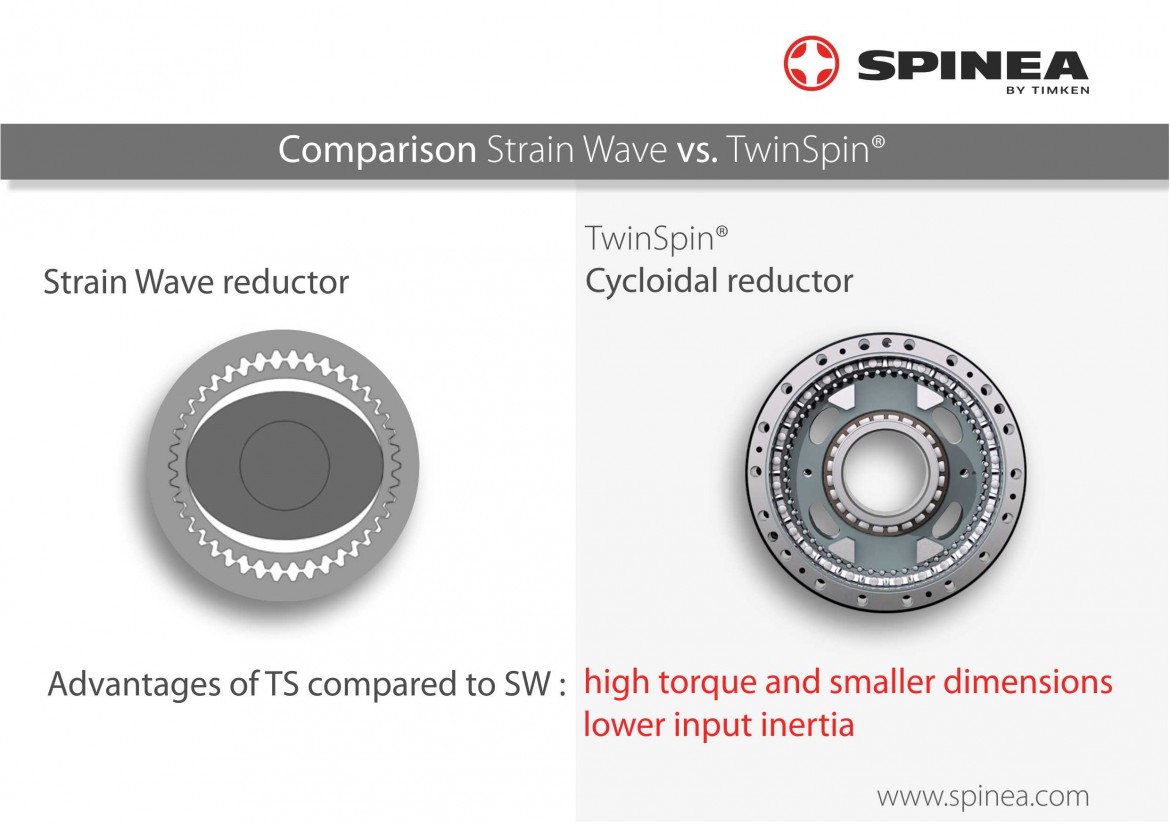
As seen on the above figures, reduction gears TwinSpin® use only rigid components for speed reduction and transfer of forces and don´t contain elastically deformable component - Flexspline. In this light, TwinSpin® reduction gears are principally more like cycloidal drives.
SW gears are dominant mainly in smaller sizes and torques. TwinSpin® line products have introduced the cycloidal principle advantages into this area too. The smallest reduction gears TwinSpin® are of diameter 60 mm.
The gearing ratio value represents another difference between TwinSpin® and SW. It is an even number in the case of SW, vs odd number in the case of TwinSpin®.
The following differences should be considered when making the design of drive systems with bearing reduction gears TwinSpin®.
Torque - in the case of TwinSpin®, it doesn´t depend on gear ratio. That means a reduction gear with ratio 33 will have the same torque as a reduction gear with ratio 85. Principally, torque depends on the ratio in the case of SW gears. Torque can be by 50% smaller in case of low ratios 30-50 than in case of high ratios 100-120.
Reduction gear dimensions – the cycloidal principle of bearing reduction gears TwinSpin® enables higher torque within smaller gear diameter than in the case of the SW principle. Considering the similar size of gears, reduction gears TwinSpin® reaches higher torque and higher torsion stiffness.
Input inertia - Wave generator at in SW reduction gear is of rather a big diameter, resulting in higher inertia. With the same rated torque, bearing reduction gears TwinSpin® has lower input inertia. Low inertia is important for drive dynamics.
Neither ratcheting nor buckling phenomena exist in gears TwinSpin® as it is in the case of SW reduction gears. Hence, the position is not lost and deformation doesn´t occur in the reduction gear component even at very high overloading.
Reduction gears TwinSpin® allows for up to 5 times the reduction gear overloading without loss of its functionality or damage to internal components. Robust roller bearings used in reduction gears TwinSpin® guarantees precise and stiff position of the transmission mechanism.
Even high overloading by tilting moment doesn´t affect the reduction gear performance. In the case of SW reduction gears, exceeded maximum values of tilting moment could affect the reduction gear functionality.
Unit gear – high precision reduction gears TwinSpin® are supplied as the Units with integrated axial -radial exit bearing. They cannot be supplied as the component sets as in the case of SW reduction gears.
Method of torque transmission affects also the lubrication. To perform properly, reduction gears TwinSpin® use different types of lubricants than SW reducers.
In conclusion, every application has its own specific aspects and customers should therefore consider all of them, as well as requirements put on the drive unit.
Company SPINEA, s.r.o. will be glad to provide you with further information on how to correctly design equipment with high precision reduction gears of TwinSpin® brand.


 SK
SK DE
DE IT
IT RU
RU CN
CN